Alec Cowan
Producer, Soundside
About
Alec Cowan is a producer for Soundside. His interests have brought many eclectic stories to the program, and his segments gravitate toward history, technology, arts and culture, and the environment. Proud to be KUOW's unofficial "boat guy."
Prior to joining Soundside, Alec wore many hats at KUOW. He was a producer for The Record with Bill Radke and Primed seasons two and three . He also reported an episode of SoundQs detailing how prohibition forever changed Seattle policing and assisted with reporting a breakthrough cold case solved with the use of genetic genealogy.
Before joining KUOW Alec worked in NPR's Story Lab, where he helped pilot the Louder Than a Riot podcast, about hip-hop and mass incarceration, and assisted in producing a story on volunteerism in Iraq for Rough Translation. Originally from Grand Junction, Colorado, his roots in the Northwest begin in Eugene, where he studied English and philosophy at the University of Oregon and worked as a news reporter for NPR member station KLCC. He is likely neglecting his saxophone, growing book collection, and expanding personal project list in favor of boosting his online Xbox ranking.
Location: Seattle
Languages Spoken: English
Pronouns: he/him/his
Podcasts
Stories
-

Government
WA bill aims to make dancing in strip clubs safer. What would change?
Dancers say working in Washington strip clubs carries a lot of risks, from the physical danger of aggressive customers to the thin financial margins that put dancers at an increased risk of sex trafficking. To try and mitigate some of these issues, Washington legislators are considering SB 6105 – what some are calling the “strippers' bill of rights.”
-

Government
Investigation finds utility's security light at fault for devastating Gray Fire
In a report released last week, the Washington Department of Natural Resources says the initial sparks came from a security light mounted on an Inland Power and Light pole. Those sparks ignited nearby brush and the fire quickly raged out of control. The Gray Fire burned 10,000 acres last August, forcing thousands to evacuate and destroying hundreds of homes.
-

Environment
Rock climbing could change to protect the wild — but will that make it more dangerous?
What does it mean for land to be “wild?” It’s a question that federal land managers have thought about since the Wilderness Act of 1964, which defined wilderness as areas “...untrammeled by man, where man himself is a visitor who does not remain.” Our national parks and public lands have visitor centers, fire lookouts, and other approved "installations" that help us enjoy the wild safely. But just what defines an installation has become the center of a recent debate between rock climbers and conservationists.
-

Government
Bremerton walks a fine line between encampment sweeps and available shelters
As homelessness grows around the region, communities are struggling to keep up with a spreading encampment crisis. In Bremerton, the largest city in Kitsap County, growing encampments have forced the city to reconcile with a lack of available shelter space throughout the county.
-
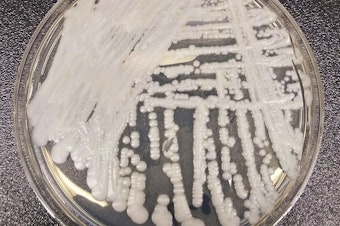
Health
Four cases of rare fungus found in WA. Here's what you should know about it
Last month the first-ever local outbreak of Candida auris, a deadly fungus, was reported in Washington State. So far, four cases of infection from the fungus have been linked to Kindred Hospital in Seattle’s First Hill neighborhood. Cases of C. auris -- which was first identified in Japan in 2009 -- have risen throughout the United States since 2016.
-

Law & Courts
How an Indigenous rights battle in WA changed tribal law, from fishing to culverts
Fifty years ago, a landmark federal court case brought against Washington state reaffirmed the treaty rights of Native Americans to fish in traditional waters and shorelines. From culvert rehab to dam removal, 1974's "Boldt Decision" has expanded far beyond fishing to legally empower tribes' ability to protect natural resources.
-

Science
Could studying how dogs age help us understand the ways humans do?
Dogs share so much of their lives with humans and can develop the same health conditions we do, like dementia or diabetes. Those similarities drove researchers to wonder if our medical science can help dogs live longer — and if maybe, our furry friends could tell us something about how we age, too.
-

Science
Woolly dogs once provided fleece for Coast Salish tribes. What happened to them?
Outside of alpacas, woolly dogs were one of the few indigenous animals providing wool in the Americas. And for centuries, woolly dogs were at the center of tribal life throughout the Coast Salish world. Since the 19th century, however, these dogs are considered extinct. Today, a resurfaced specimen at the Smithsonian Institution is helping broaden the scientific and tribal understanding of the woolly dog's genetics and role in Coast Salish life.
-

Environment
Looking back and looking ahead: the 50-year anniversary of the Endangered Species Act
Since it was passed, the ESA has listed more than 1,600 species for protection, and the overwhelming majority of listed animals have been saved from extinction. What have we learned in the last 50 years about how we can better protect the environment – and what lessons can we take with us into the next 50 years of the Endangered Species Act?
-

Business
After Alaska flight loses door plug at 16,000 feet, questions about Boeing Max planes linger
On Friday, 20 minutes after takeoff and at an elevation of 16,000 feet, a door plug on the side of Alaska Airlines Flight 1282 ripped off midair. As oxygen masks dropped from the ceiling, some of the 171 passengers took videos on their phones of the gaping hole in the side of the jet. After quickly circling back to Portland, Ore., the plane landed safely. Now all the attention is on what could have happened aboard that Boeing 737 Max 9.
